Qdrant Vector Store
Overview
The Qdrant Vector Store node in AnswerAI allows you to upsert embedded data and perform similarity searches using Qdrant, a scalable open-source vector database written in Rust. This node enables efficient storage and retrieval of high-dimensional vectors, making it ideal for various AI and machine learning applications.
Key Benefits
- Scalable and efficient vector storage and retrieval
- Support for both local and cloud-hosted Qdrant instances
- Flexible configuration options for advanced use cases
How to Use
- Add the Qdrant Vector Store node to your AnswerAI canvas.
- Connect the required inputs:
- Document: Connect to a Document Loader node (optional)
- Embeddings: Connect to an Embeddings node
- Configure the node settings:
- Qdrant Server URL: Enter the URL of your Qdrant server
- Qdrant Collection Name: Specify the name of the collection to use
- Vector Dimension: Set the dimension of your vectors (default: 1536)
- (Optional) Configure additional parameters:
- Upsert Batch Size: Set the batch size for upserting documents
- Similarity: Choose the similarity measure (Cosine, Euclid, or Dot)
- Additional Collection Configuration: Provide JSON configuration for advanced settings
- Top K: Specify the number of top results to fetch
- Qdrant Search Filter: Add a JSON filter to refine search results
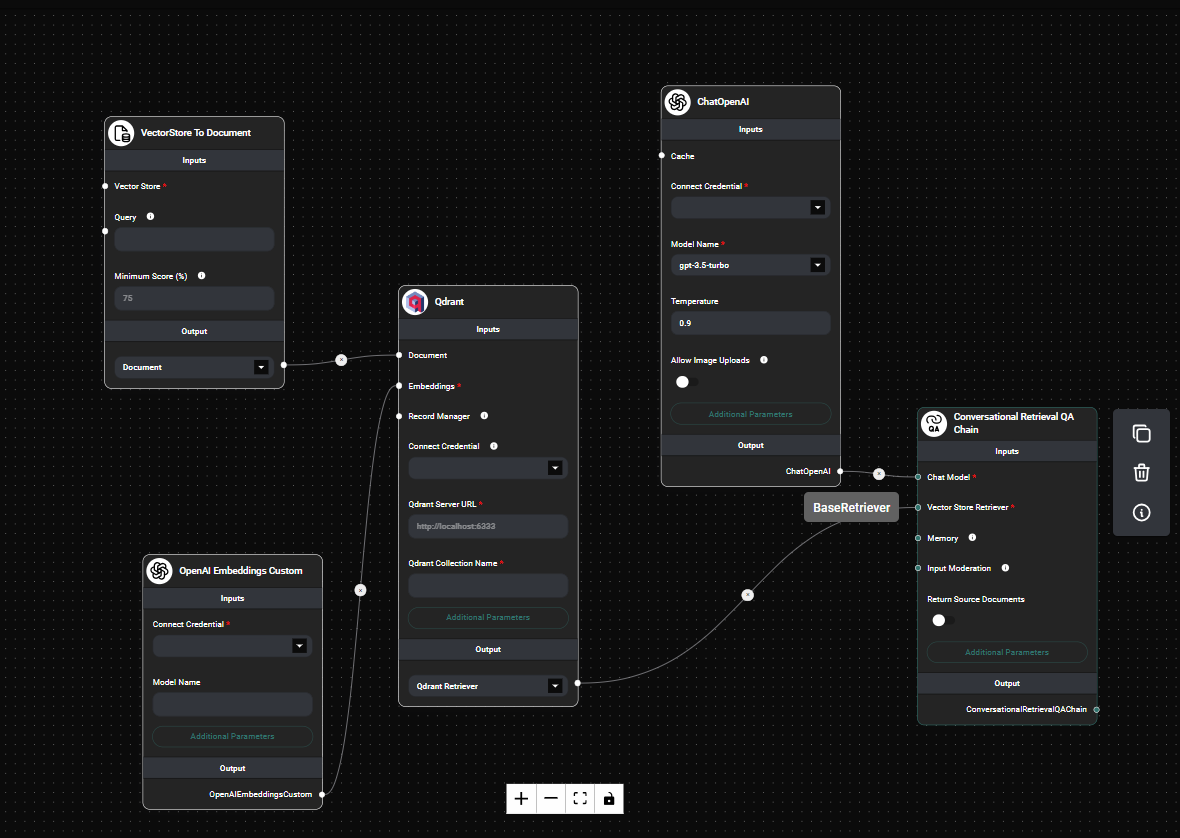
Qdrant Vector Store node configuration & Drop UI
Tips and Best Practices
- Use a Record Manager to prevent duplication when upserting documents.
- Adjust the Upsert Batch Size for optimal performance when dealing with large datasets.
- Experiment with different similarity measures to find the best fit for your use case.
- Utilize the Qdrant Search Filter to narrow down search results based on metadata or other criteria.
Troubleshooting
-
Connection issues:
- Ensure that the Qdrant Server URL is correct and accessible.
- Check if the API key (for cloud-hosted instances) is valid and properly configured.
-
Performance problems:
- Try adjusting the Upsert Batch Size to find the optimal balance between speed and resource usage.
- Verify that the Vector Dimension matches the output of your Embeddings node.
-
Unexpected search results:
- Double-check the Qdrant Search Filter syntax for any errors.
- Ensure that the Top K value is appropriate for your use case.
Advanced Usage: Filtering
Qdrant supports advanced filtering capabilities to refine your search results. Here's how to use filters effectively:
-
Each document in your vector store can have metadata associated with it, such as a
sourcefield. -
To filter results based on metadata, use the "Qdrant Search Filter" option in the node configuration.
-
The filter should be provided as a JSON object. For example, to filter documents from a specific source:
{
"should": [
{
"key": "metadata.source",
"match": {
"value": "apple"
}
}
]
}
Qdrant Search Filter configuration & Drop UI
This filter will return only documents where the metadata.source field matches "apple".
- You can create more complex filters using Qdrant's filter syntax, which supports nested conditions, range queries, and more. Refer to the Qdrant documentation for advanced filtering options.
By leveraging filters, you can create more targeted and relevant search results, improving the overall performance of your AnswerAI workflows.
Remember to test your filters thoroughly to ensure they're working as expected in your specific use case.