Code Text Splitter
Overview
The Code Text Splitter is a powerful feature in AnswerAI that allows you to split code documents into smaller, manageable chunks based on language-specific syntax. This tool is particularly useful when working with large codebases or when you need to process code in a more granular manner.
Key Benefits
- Language-specific splitting: Accurately splits code based on the syntax of the chosen programming language.
- Customizable chunk size: Allows you to control the size of each code chunk for optimal processing.
- Improved code analysis: Enables more efficient analysis and processing of large codebases.
How to Use
- In the AnswerAI Studio, locate the "Text Splitters" category in the node palette.
- Drag and drop the "Code Text Splitter" node onto your canvas.
- Connect the Code Text Splitter node to your input source (e.g., a document loader or another node that outputs text).
- Configure the Code Text Splitter node: a. Select the appropriate programming language from the "Language" dropdown menu. b. (Optional) Adjust the "Chunk Size" to set the number of characters in each chunk (default is 1000). c. (Optional) Set the "Chunk Overlap" to determine the number of characters that overlap between chunks (default is 200).
- Connect the output of the Code Text Splitter to the next node in your workflow.
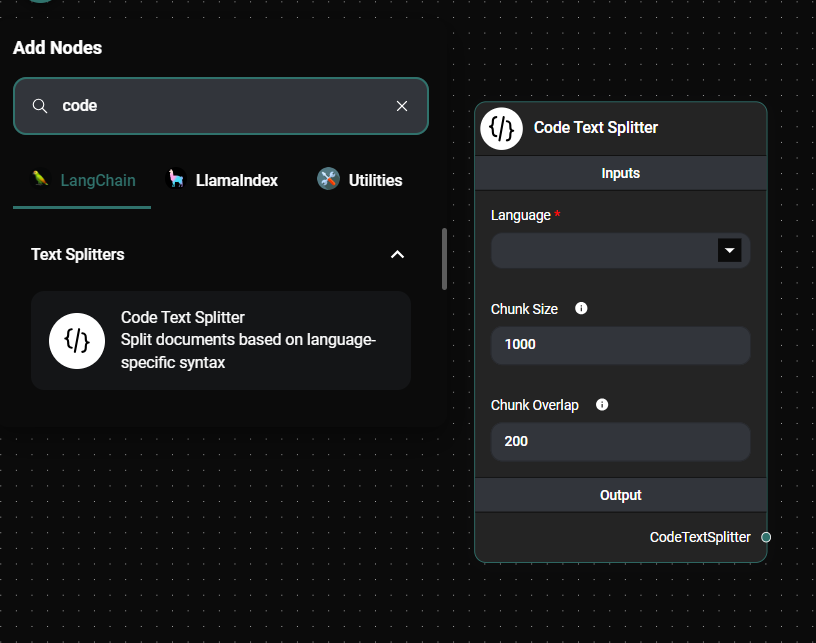
Code Text Splitter & Drop UI
Supported Languages
The Code Text Splitter supports the following programming languages:
- C++ (cpp)
- Go (go)
- Java (java)
- JavaScript (js)
- PHP (php)
- Protocol Buffers (proto)
- Python (python)
- reStructuredText (rst)
- Ruby (ruby)
- Rust (rust)
- Scala (scala)
- Swift (swift)
- Markdown (markdown)
- LaTeX (latex)
- HTML (html)
- Solidity (sol)
Tips and Best Practices
- Choose the correct language: Ensure you select the appropriate programming language for your code to get the most accurate splitting results.
- Experiment with chunk sizes: Adjust the chunk size based on your specific use case. Smaller chunks may be better for detailed analysis, while larger chunks can provide more context.
- Consider chunk overlap: Use chunk overlap to maintain context between chunks, especially for languages with complex syntax or long function definitions.
- Combine with other nodes: Use the Code Text Splitter in combination with other nodes, such as embeddings or vector stores, to create powerful code analysis workflows.
Troubleshooting
- Incorrect splitting: If the code isn't split correctly, double-check that you've selected the right programming language.
- Performance issues: If processing is slow, try increasing the chunk size to reduce the total number of chunks.
- Loss of context: If important context is lost between chunks, increase the chunk overlap value.
Remember that the effectiveness of the Code Text Splitter can vary depending on the complexity and structure of your code. Experiment with different settings to find the optimal configuration for your specific use case.