Advanced Structured Output Parser
Overview
The Advanced Structured Output Parser is a powerful tool in AnswerAgentAI that allows you to parse the output of a language model into a predefined structure. By providing a Zod schema, you can ensure that the model's output adheres to a specific format, making it easier to work with structured data in your workflows.
Key Benefits
- Ensure consistent and structured output from language models
- Easily validate and transform complex data structures
- Improve the reliability of your AI-powered applications
How to Use
- Add the "Advanced Structured Output Parser" node to your AnswerAgentAI canvas.
- Configure the node settings:
- Set the "Autofix" option if you want the parser to attempt fixing errors automatically.
- Provide a Zod schema in the "Example JSON" field.
- Connect the parser node to your language model output.
- Use the parsed output in subsequent nodes or as the final result of your workflow.
Advanced Structured Output Parser node configuration panel & Drop UI
Tips and Best Practices
- Start with a simple schema and gradually increase complexity as needed.
- Use the "Autofix" option cautiously, as it may sometimes produce unexpected results.
- Test your schemas thoroughly with various inputs to ensure robustness.
- Leverage Zod's rich set of validation and transformation methods for advanced use cases.
Troubleshooting
- If you encounter a "Error parsing Zod Schema" message, double-check your schema syntax and ensure all required imports are present.
- If the parser fails to extract the expected data, review your language model's prompt to ensure it's generating output in the correct format.
Zod Schema Examples
Here are some examples of Zod schemas for different use cases:
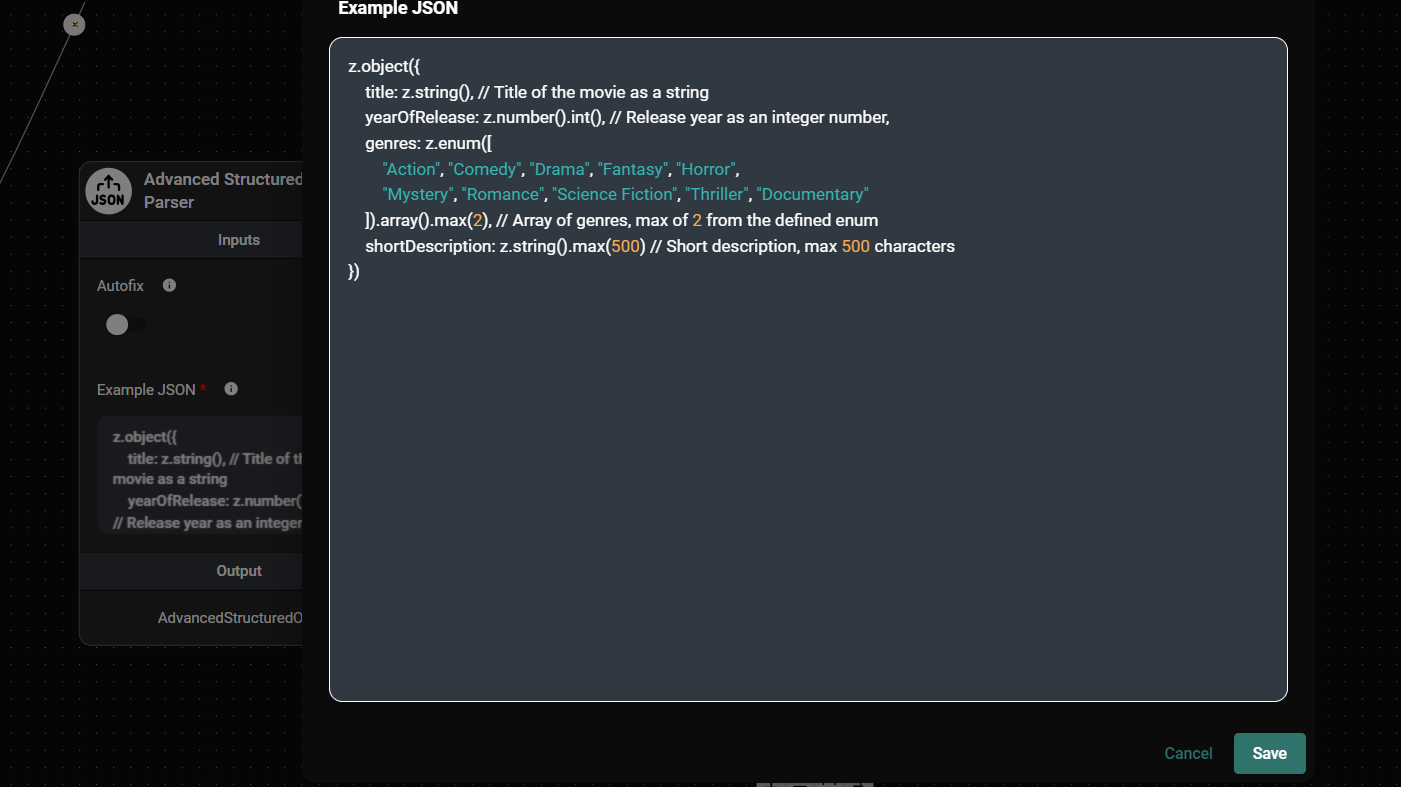
1. Movie Information
This schema defines a structure for movie information, including a title, release year, genres (limited to 2), and a short description.
z.object({
title: z.string(),
yearOfRelease: z.number().int(),
genres: z
.enum(['Action', 'Comedy', 'Drama', 'Fantasy', 'Horror', 'Mystery', 'Romance', 'Science Fiction', 'Thriller', 'Documentary'])
.array()
.max(2),
shortDescription: z.string().max(500)
})
2. User Profile
This schema represents a user profile with validation for username length, email format, age range, number of interests, and verification status.
z.object({
username: z.string().min(3).max(20),
email: z.string().email(),
age: z.number().int().min(13).max(120),
interests: z.array(z.string()).min(1).max(5),
isVerified: z.boolean()
})
3. Product Catalog
This schema defines a product catalog with multiple products, each having an ID, name, price, category, stock status, and optional tags.
z.object({
products: z
.array(
z.object({
id: z.string().uuid(),
name: z.string(),
price: z.number().positive(),
category: z.enum(['Electronics', 'Clothing', 'Books', 'Home & Garden']),
inStock: z.boolean(),
tags: z.array(z.string()).optional()
})
)
.min(1)
.max(100)
})
4. Weather Forecast
This schema represents a weather forecast with location, date, temperature in Celsius and Fahrenheit, weather conditions, precipitation probability, and wind speed.
z.object({
location: z.string(),
date: z.string().regex(/^\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2}$/),
temperature: z.object({
celsius: z.number(),
fahrenheit: z.number()
}),
conditions: z.enum(['Sunny', 'Cloudy', 'Rainy', 'Snowy', 'Windy']),
precipitation: z.number().min(0).max(100),
windSpeed: z.number().nonnegative()
})
5. Blog Post
This schema defines a structure for a blog post, including title, author, publish date, content, tags, and optional comments.
z.object({
title: z.string().max(100),
author: z.string(),
publishDate: z.string().datetime(),
content: z.string().min(100),
tags: z.array(z.string()).max(10),
comments: z
.array(
z.object({
user: z.string(),
text: z.string().max(500),
timestamp: z.string().datetime()
})
)
.optional()
})
By using these Zod schema examples as a starting point, you can create custom schemas tailored to your specific use cases in AnswerAgentAI. Remember to adjust the validation rules and structure to match your exact requirements.